Speed up your Windows PC by disabling Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)
Does your Windows PC (XP or higher) ever suddenly slow down to a standstill, despite the fact that you weren’t doing anything different than before? Well, this can be due to a variety of causes.
One of them is the Background Intelligent Transfer Service (aka BITS). This process will start using a great deal of your disk usage and CPU, seemingly out of nowhere. Let’s look at how to diagnose your problem, disable that process, and get your PC speed back.
Diagnose the problem
Before we proceed, I must again mention that there can be a variety of causes for periodic lockups and slowdowns. This is just one of them. There are a couple of ways to look into this.
- When your computer is acting up, open up the task manager by pressing CTRL+ALT+DEL and choosing it from the menu that pops up, if applicable. Use this quick tutorial to learn how to check disk usage from there if you are using Windows 7 or earlier.
- Download a system monitoring application like Rainmeter to have your currently running processes and the like displayed live on your desktop. Remember that adding another program to the mix may come at the cost of speed.
In each case, take note of the programs/processes that are using a high-percentage of CPU, RAM, and disk usage. I caught Background Intelligent Transfer Service using up 50% of my disk usage and a large portion of my CPU usage at the exact times my computer would slow down to a freeze.
Background Intelligent Transfer Service will appear in these situations as svchost.exe. In Windows 8, it will be one of several processes that is called Service Host. An important thing to note is that svchost.exe is a kind of catch-all name for several Windows processes and that its presence in your task manager is not necessarily a problem nor is it necessarily BITS. The key symptom to look for is high disk usage.
To see if BITS is one of the processes involved, you’ll want to expand that svchost.exe process. The method for this depends on which version of Windows you’re using.
Windows 7 and older:
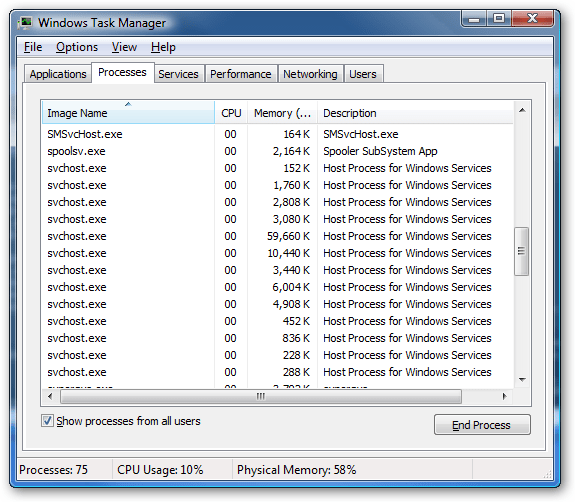
When looking at the collection of svchost.exe processes, identify the one that concerns you most (due to CPU and/or disk usage) and right click on it. Then, go to the bottom of the pop-up menu and select “Go to service(s).”
Image from HowToGeek
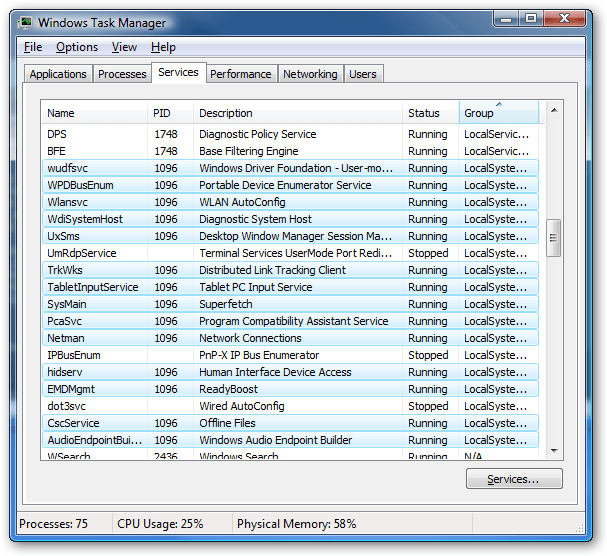
You will see the services involved in that task highlighted in the “services” tab. If Background Intelligent Transfer Service is one of them, you might have found the culprit. The full name will be under the “description” column. Here’s an example of how that might look:
Image from HowToGeek
In Windows 8:
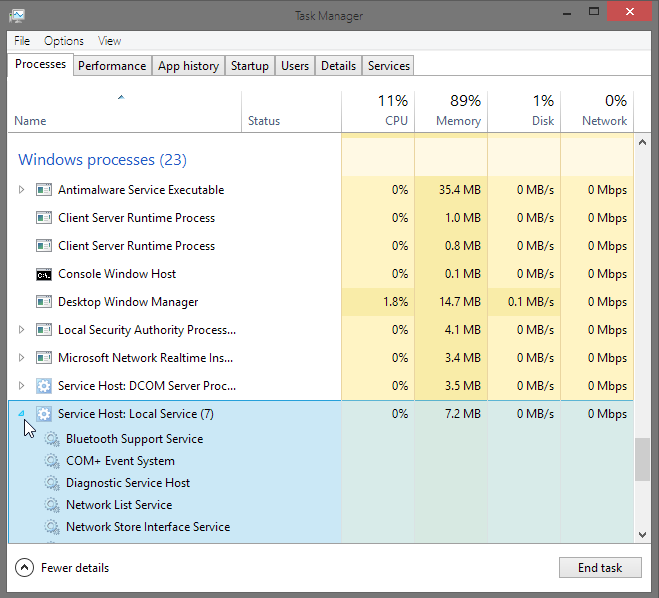
It’s much simpler in Windows 8. Open Task Manager, and scroll to the bottom of the list of process to get to the list of Windows processes. Optionally, you can order all processes by CPU, RAM, or disk usage, in which case you’ll navigate to the offending process. You can expand the Service Host process by clicking the arrow to its left and then see the services it is responsible for.
Before you disable BITS, shouldn’t you know what it is?
As a savvy tech person, you probably don’t want to just blindly disable things just because they make your computer work hard. You’re correct to feel that way. Background Intelligent Transfer Service is built into Windows for a good reason and many services like it simply cannot be disabled.
BITS is a portion of the operating system that automatically updates certain Windows components, like Windows Defender and Windows Update. The most common reason for it to start up is because it is checking for an update to a Windows program or the system itself and then proceeds to download.
The reason BITS is “intelligent” is because it will not monopolize your Internet connection. If you aren’t using the Internet, it will use all of your bandwidth, but if you are, it will only use whatever bandwidth is left over. However, the process of downloading can affect more than just your Internet speed. Your computer’s ability to read the hard drive or run other processes can be impaired if BITS is using too much of the processing power or hard drive at once.
Many people will never have a problem with this, because it is usually good at staying out of your way. However, on mid-range and low-end computers as well as older computers, the machine may not be able to handle this level of multitasking. If you have a lot of browser tabs open or are doing a few things already, your system may not be able to accommodate BITS without slowing down or freezing momentarily.
Rather than actually disabling BITS, we’re going to change its settings so that it only starts up when you have expressly told it to work. You have to install updates to your computer and programs sometimes, after all.
Change the BITS settings
Now that you know you want to get rid of Background Intelligent Transfer Service, you have to go do it. There are a few different steps involved.
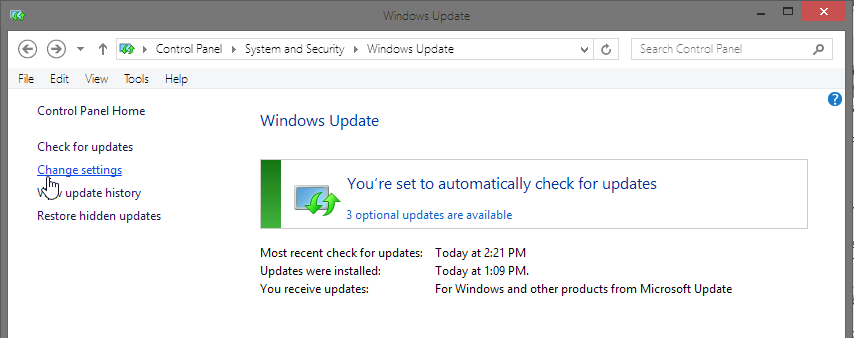
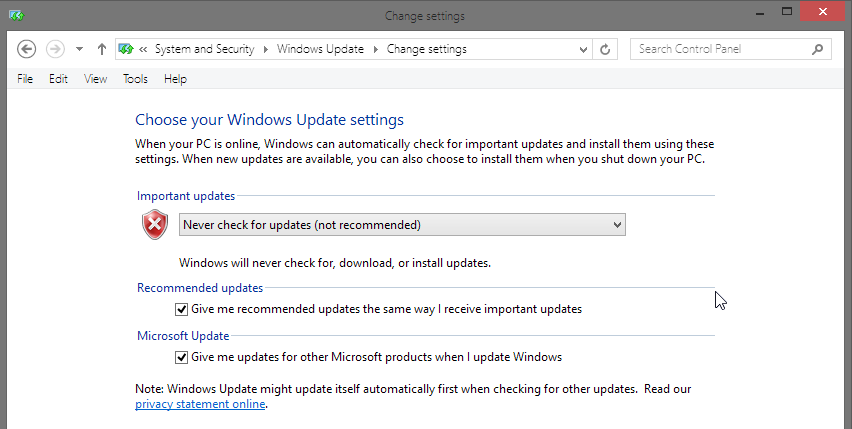
First, we need to turn off automatic software updates. To do this, go to Control Panel -> System and Security -> Windows Update. From there, click on “Change settings” as you see below:
In the settings menu, you want to “never check for updates” which they say is not recommended. It’s not recommended because updates are important. Remember to make a habit of checking for updates every day or so after disabling automatic updates!
The reason we have turned off automatic update checking is because this is the most common trigger of the Background Intelligent Transfer Service. If you don’t do this, it will automatically be turned on regularly whenever Windows checks for updates. This is about giving you control over when this process runs; don’t lose it by leaving automatic updating enabled.
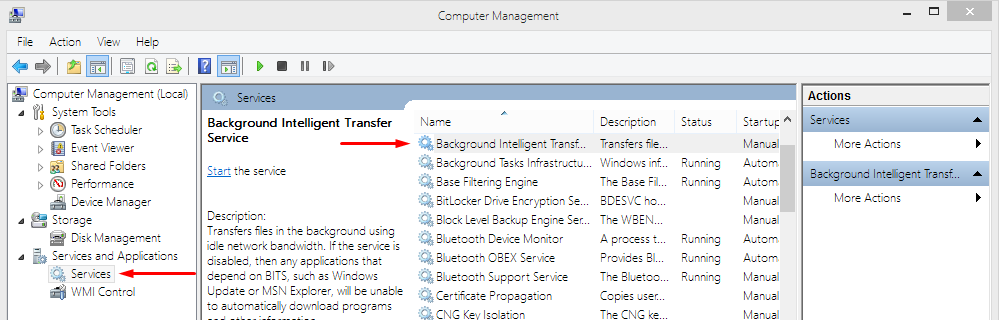
Next, you need to go to the Computer Management Console. To get there, go to Control Panel -> Performance and Maintenance -> Administrative Controls -> Computer Management. Or you can simply do a system search for “Computer Management” from the start menu (Windows 7 or older) or by pressing Windows+S keys (Windows 8).
Once you’re there, click on “services” on the bottom of the left-hand sidebar. You should see something like the image below. Navigate to Background Intelligent Transfer Service, right click, and press “properties.”
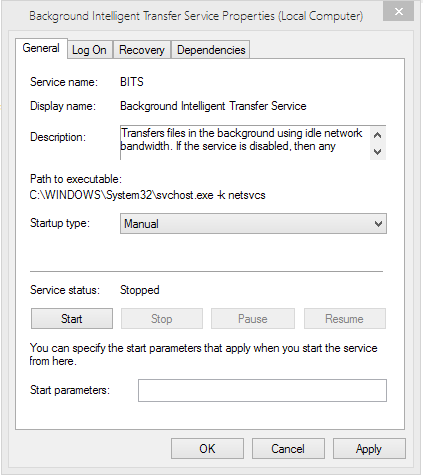
After pressing properties, you should get a prompt like the one below. There are two things to do:
- Stop the process. Just press the “Stop” button.
- Change the “startup type” selection to “Manual.” This allows the process to run, but only when you ask it to by starting an update.
Still having problems?
If you’re still dealing with lockups/freezes/slowdowns, BITS may not have been the problem, or at least not the only one. Repeat the diagnosis steps in the early portion of this article to see if there’s another process at fault. You should also observe carefully to see if this happens when you do any particular action or if it really appears to be random.
Featured image by Ryan Hyde (Flickr).
COMMENTS
Search
Related Posts
Recent Posts
- Make Prism.js show line numbers by default (without CSS classes)
- Hemingway App 3.0 update review: A gimmick becomes a real app
- Hugo vs. WordPress page load speed comparison: Hugo leaves WordPress in its dust
- Hemingway App 2.0 update: A worthwhile update comes with unfortunate price hike
- How to view academic journal articles off campus using your library's proxy
categories
Support This Site
Bitcoin Donations:18DP9TGdPN5usTKMRMfPk6Q2mSr4mAz8NJLitecoin Donations:
LPKQbDPykwjXr5NbXfVVQH9TqM5C497A16